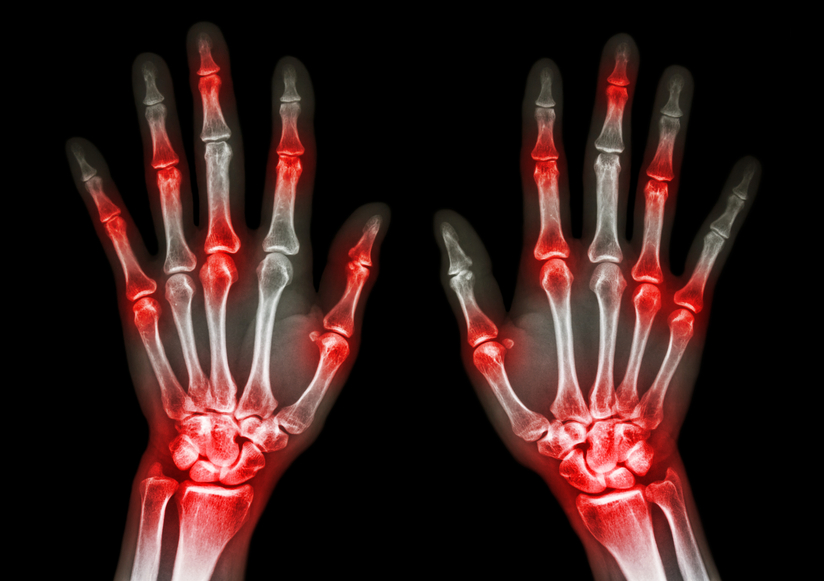
Research into the diet of people living with rheumatoid arthritis has found that although there is no dietary cure for RA, some foods may help control inflammation associated with the painful condition.
There are many types of arthritis affecting more than 50 million adults in the United States with symptoms that can include swelling, pain and stiffness of joints sometimes leading to a loss of mobility and range of motion. Arthritis is more common among women and occurs more frequently in older age.
Inflammation is one of the sources of the pain and if left untreated, can cause joint erosion. In addition to medication, physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight, diet can play a key role in combating inflammation in the body.
According to the Arthritis Foundation, the best foods for arthritis are included in a Mediterranean-style diet. Fish, with omega-3 fatty acids fight inflammation and should be included at least twice a week in a good diet. Salmon, tuna, mackerel and herring are healthy choices. Other foods that help reduce inflammation include soybeans (tofu or edamame), olive, avocado, and walnut oil, cherries, low fat dairy or leafy greens for bone strength, broccoli, green tea, citrus fruits, whole grains, red, kidney or pinto beans, garlic and nuts.
Food that can cause inflammation and which can also lead to other chronic conditions should be avoided. These “trigger” foods include sugar, saturated fats, trans fats, omega 6 fatty acids found in corn, peanut, vegetable oil and mayonnaise, refined carbohydrates, msg, gluten and casein (in those with a gluten or dairy intolerance), aspartame and alcohol. Increasing the amount of fruits and vegetables you consume while reducing harmful foods may help alleviate some of the symptoms of arthritis.
For more information about how diet affects arthritis, visit http://www.arthritis.org/living-with-arthritis/arthritis-diet/ .




Add Your Voice
0 Comments
Join the Discussion