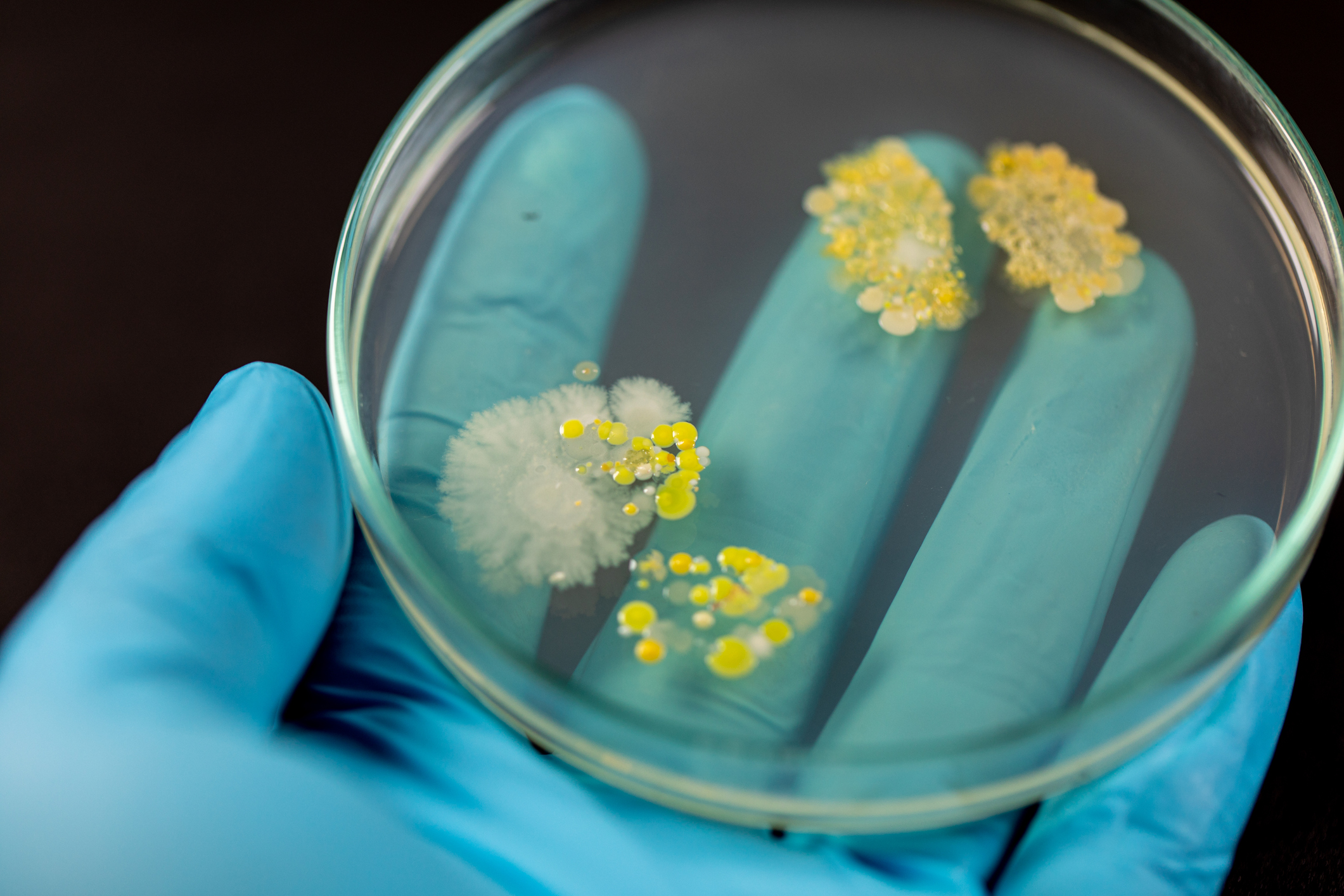
Even if you haven’t watched HBO’s The Last of Us, you might be concerned about a growing outbreak of drug-resistant and potentially deadly fungal infections spreading rapidly throughout U.S. healthcare facilities. The fungus is a type of yeast called Candida auris, or C. Auris, which can cause severe illness in people with a compromised immune system.
According to a recent NBC News report, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention found in a recent study that the number of people diagnosed with C. auris infections has been rising at an “alarming rate” since it was first identified in the U.S. in 2016. The surge in infection rates, and in new regions, has CDC researchers concerned. Since November, at least 12 people in Mississippi have been infected with C. auris, with four potentially associated deaths. Ongoing transmission has been identified at two long-term care facilities and other healthcare institutions.
Because C. auris is a multi-drug resistant organism, infection is more widespread in long-term care facilities where residents may be vulnerable to severe illness. Many elderly adults in assisted living communities have multiple chronic health problems and a weakened immune system.
C. auris fungus can be found on the skin, and throughout the body. According to the CDC, it is not a threat to healthy people, but about one-third of those who do become ill with C. auris will die. Because the fungus can survive on surfaces, hospitals and care facilities will need to be vigilant about disinfecting bedding, chairs, medical equipment, walls and floors with bleach and UV light. The CDC warns that C. auris poses an “urgent threat”, and spreads easily in healthcare facilities, especially among residents with indwelling medical devices or mechanical ventilators.
Learn more about C. auris by following this link to the CDC website. The most common symptoms of C. auris infection include fever and chills that don’t improve after antibiotic treatment for a suspected bacterial infection. Only a lab test can diagnose infection. Families and healthcare personnel should practice excellent hand hygiene and wear gowns and gloves when coming into direct contact with an infected patient.




Add Your Voice
0 Comments
Join the Discussion