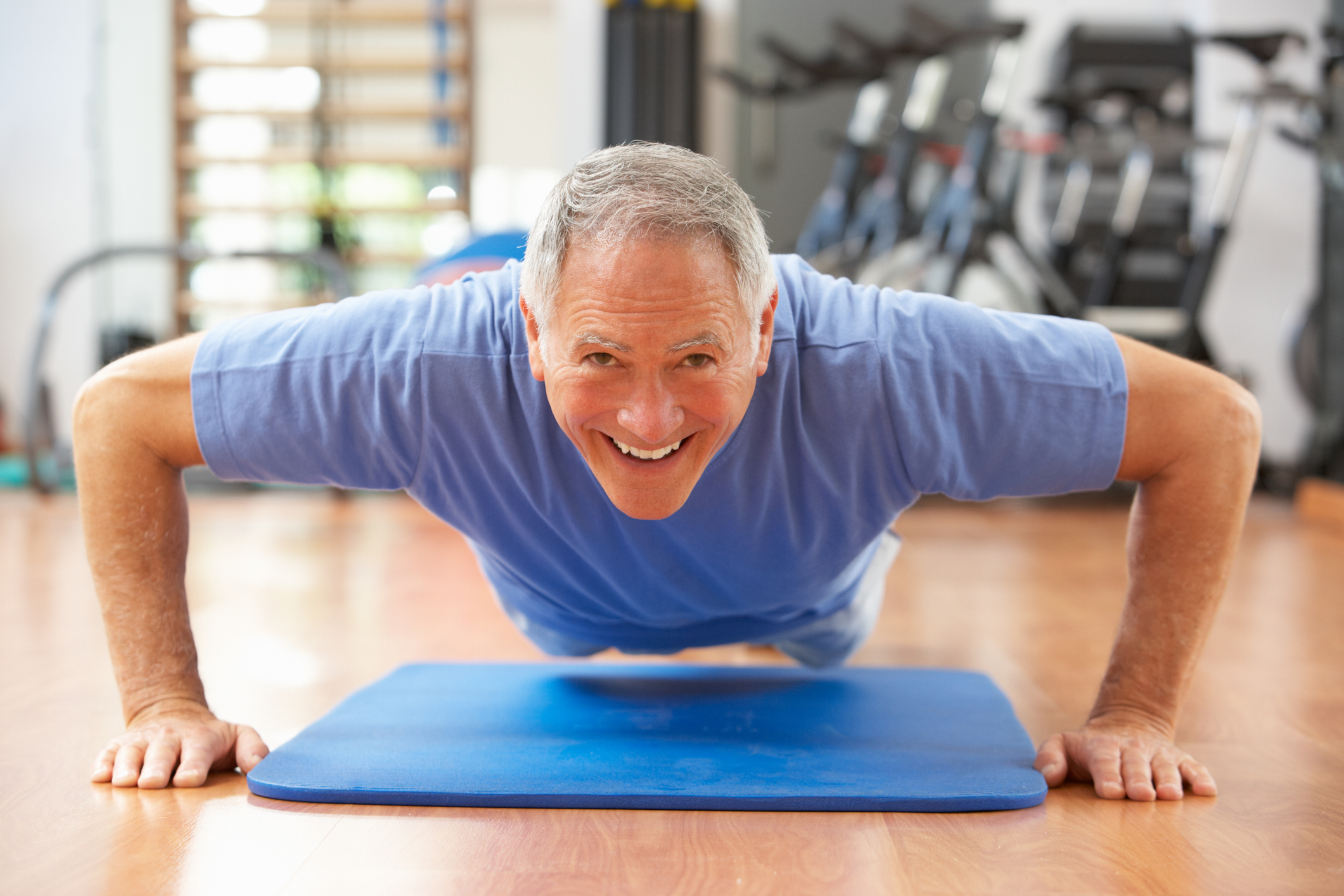
Staying physically active in middle and older age is important to help prevent loss of function and chronic illness but a new study has set a new benchmark for heart health in men, and it’s the number of push-ups a 40ish man can perform in a row.
According to a study, published online in the JAMA Network Open, from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, men who can do more than 40 push-ups consecutively have a 96 percent reduced
The study tracked 1,100 active male firefighters over a period of 10 years with an average age of 40 at the start of the study. Each year, the men had a physical and filled out health questionnaires. During the following decade, 37 men developed heart problems and researchers found that the number of push-ups a man could perform predicted their heart health better than a standard treadmill test. The test may not be an accurate predictor of heart health for some men with injuries that would prevent them from performing push-ups. A traditional stress test, performed on a treadmill can also help doctors determine if the blood supply in the arteries is reduced and help predict the risk of heart attack.
Whatever test your doctor orders, staying physically active with at least 30 minutes a day of aerobic activity and strength training on at least two days a week along with eating a health Mediterranean-style diet can help control weight, blood sugar, blood pressure and cholesterol. Your doctor may recommend a stress test if you have signs or symptoms of coronary artery disease or an irregular heart rhythm. A stress test is generally safe but should be done with medical supervision.





Add Your Voice
0 Comments
Join the Discussion