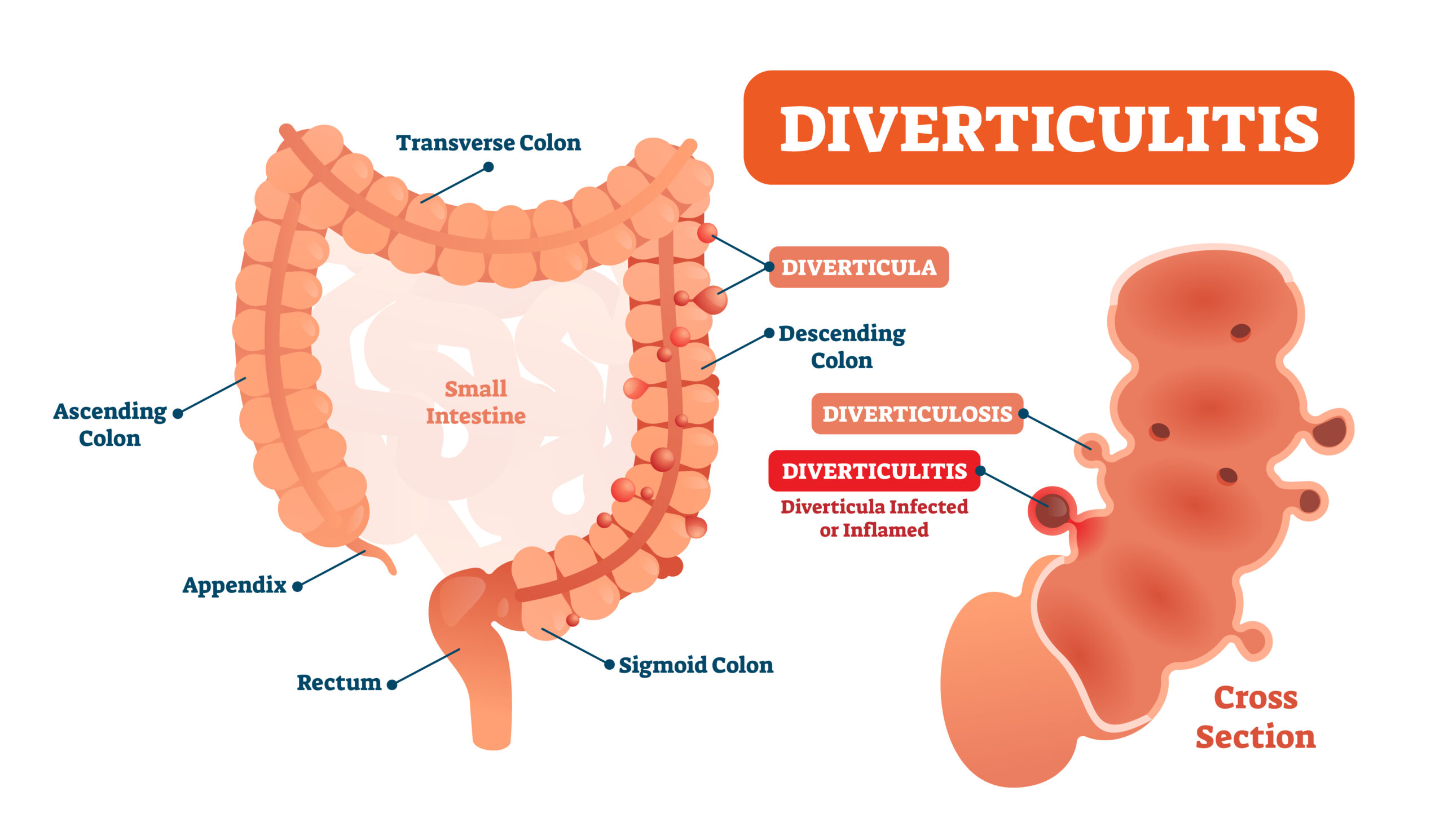
It may not be a pleasant subject to discuss but because 70 percent of people over the age of 80 will develop the condition, diverticulitis or a diverticular bleed is a condition that demands the attention of older adults. And the traditional advice for patients with the condition to avoid eating nuts, corn, popcorn and seeds has been questioned based on new research, as has the need for aggressive treatment included antibiotics or surgery.
Although there are times when surgery or aggressive antibiotic treatment is necessary for chronic or recurrent diverticulitis, studies have shown these treatments may be overused. In recent years, hospital admissions for elective diverticulitis surgery have increased between 25 and 30 percent.
According to the Harvard Health Blog, as many as a third of American adults have diverticulosis, a common condition in which pouches form in the muscular wall of the colon. If the pouches become inflamed and infected, they may bleed, cause lower abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation or fever. It doesn’t happen frequently however, only in about 4 percent of the time, and adults can lower their risk with several lifestyle changes.
Tips to reduce the risk for diverticulitis
- Eat a high fiber diet to maintain colon health and prevent constipation; aim for 25-30 grams of dietary fiber each day. Increase intake gradually to avoid an intestinal upset.
- Cut out cola and added sugars which can worsen symptoms of diverticulitis.
- Maintain a healthy weight; obesity is a risk factor for diverticulitis.
- Get regular exercise; aim for 150 minutes of moderate physical activity each week.
- Limit red meat, processed foods and too much alcohol
- Drink plenty of water
Talk with your doctor about a liquid, low fiber diet if you have a mild case of diverticulitis. This will give the digestive tract time to rest and heal. More severe cases may require hospitalization. Learn more about diverticular disease and recent research by following this link to the American Gastroenterological Association Journal.




Add Your Voice
0 Comments
Join the Discussion